Introduction to Soil Fungi
Key Takeaways
By the end of this module, you should be familiar with:
- the basic structure of fungi
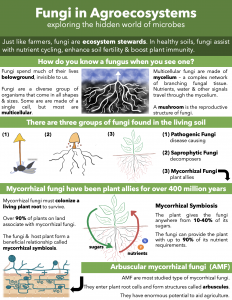
- the types of fungi found in the living soil
- the role of mycorrhizal fungi
Fungi are key microbial players in the black box of soil. In a handful of healthy soil, there are many types of fungi.

Image 1. A Handful of Healthy Soil
Just like farmers, fungi are ecosystem stewards. In balanced agroecosystems, fungi assist with nutrient cycling, and enhance soil fertility, and plant immunity. In upcoming modules, we will explore exactly how fungi can benefit agroecosystems. In this module, we will introduce fungi and focus on the key types of fungi that can improve the health of agroecosystems.

Image 2. Fungi Belowground
In agriculture today, fungi are often vilified. We often think of them as pathogens, or disease-causing organisms. In agriculture, fungal diseases (rusts, wilts, mildews, etc.) have caused significant economic hardship for farmers.
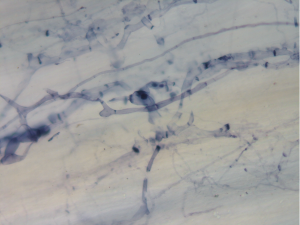
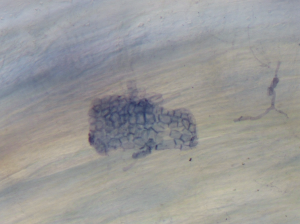
Image 3. Mycorrhizal Fungi Stained in a Plant Root
HOWEVER, this focus on fungi as pathogens is a one-sided and narrow account. Fungi have enormous potential to assist agriculture. While they can act as plant pathogens, they can also act as plant allies. In fact, fungi are some of the oldest allies of plants.
A video introduction to the fungi in the living soil
Mycology is a young natural science
As this video showed us, fungi are a very diverse group of organisms, and they come in all shapes and sizes.
The study of fungi is called mycology.
There are large gaps in our knowledge about fungi.
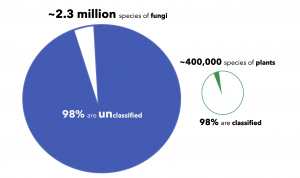
Image 4. Undiscovered Fungi
Scientists estimate that are approximately 2.3 million fungal species (this is a conservative estimate), and only 2% of fungi are classified. By comparison, there are approximately 400,000 plant species, and 98% are classified. In other words, there are at least six fungal species for every plant species on our planet.
For a long time, this astounding fungal diversity was overlooked. We are now beginning to appreciate the importance of fungi, especially in agriculture.
Mycorrhizal fungi
Mycorrhizal fungi are a type of fungi that have enormous potential to assist agriculture.
Image 5. Mycorrhizal Hypha and Arbuscule in a Plant Root
A mini quiz
A video introduction to mycorrhizal fungi
Mycorrhizal fungi have been plant allies for well over 400 million years. Today, over 90% of land plants work alongside mycorrhizal fungi.
These fungi must colonize a living plant root in order to survive. When mycorrhizal fungi colonize plant roots, they form a beneficial relationship with their plant host. This beneficial relationship is called mycorrhizal symbiosis.
Informational Handout: Fungi in Agroecosystems
Handout PFD: Fungi in Agroecosystems
Resources
- Resource from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS)
- Authored by pioneering soil ecologist, Dr. Elaine Ingham
- Introduces the three major types of soil fungi: decomposers, mutualists, and pathogens
Keep Soils Alive, Protect Soil Biodiversity
- Animation by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- Provides an introduction to soil biodiversity loss
- This is documentary directed by Chelsea Myers of Tiny Attic Productions and produced by the Soil Health Institute
- Features innovative farmers and soil health experts from throughout the U.S.
Terminology
Fungus (pl. fungi):
Non-photosynthesizing organism that lives inside soil and plant roots. Usually grows in long threads known as hyphae.
Mycelium:
The network of underground fungal filaments. Complex architecture.
Hypha (pl. hyphae):
Branching tubular filaments made by the fungi underground. Collectively called the mycelium.
Mushroom:
Fleshy fruiting body of some fungi. The usual form is a cap on top of a stalk.
Spores:
Analogous to plant seeds. Agent of fungal dispersal and reproduction.
Pathogenic Fungi:
A group of fungi that cause disease when they colonize organisms.
Saprophytic Fungi:
A group of fungi that decompose organic matter. They feed on dead plant and animal material.
Mycorrhizal Fungi:
The group of fungi in a symbiotic relationship with a plant root (myco- meaning ‘fungi’ & rhiza meaning ‘root’)
Ectomycorrhizal Fungi:
A type of mycorrhizal fungi that do not penetrate into plant roots (ecto- meaning ‘outside’).
Endomycorrhizal Fungi:
A type of mycorrhizal fungi that do penetrate into plant roots (endo- meaning ‘inside’).
Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF):
The most common type of mycorrhizal fungi with the most relevant applications to agriculture.
Arbuscule:
The specialized and highly branched organ made by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inside plant root cells. It is the site of exchange between the plant and fungi.
Image Citations
Image 1. A Handful of Healthy Soil
Alex Lintner. Photograph. May 2021. Attribution CC BY-NC 2.0.
Image 2. Fungi Belowground
Alex Lintner. Illustration. April 2021. Attribution CC BY-NC 2.0.
Image 3. Mycorrhizal Fungi Stained in a Plant Root
Alex Lintner. Illustration. April 2021. Attribution CC BY-NC 2.0.
Image 4. Undiscovered Fungi
Alex Lintner. Illustration. April 2021. Attribution CC BY-NC 2.0.
Image 5. Mycorrhizal Hypha in a Plant Root
Alex Lintner. Microscope Image. April 2019. Attribution CC BY-NC 2.0.
Image 5. Mycorrhizal Arbuscule in a Plant Root
Alex Lintner. Microscope Image. April 2019. Attribution CC BY-NC 2.0.